Useful Gemological and Jewelry Terms
/Bookmark this page! It will be updated with more terms!
Allochromatic: When color is caused by impurity elements or defects in its crystal structure rather than by an element of its basic chemical composition.
Annealing: The process of using heat to stabilize irradiated color in gemstones such as diamonds.
Asterism: Asterism is the name that was given to the phenomenon that causes gemstones to exhibit a star-like shape when cut into a cabochon. The optical phenomenon is displayed by some rubies, sapphires, and other gems (i.e. star garnet, star diopside, star spinel, etc.). The Star-effect or "asterism" is caused by the dense inclusions of tiny needlelike crystals of called rutile (also known as "silk"). The stars are caused by the light reflecting from needle-like inclusions of rutile which are aligned perpendicular to the rays of the star. Star gemstones are almost never transparent since rutile is always present in star gemstones.
Cameo: A design cut in high relief into a hard stone or shell
Collet Setiing: A Collet setting (also called a bezel setting) is a ring or rim of metal, designed to encircle the girdle of a gemstone. The upper edge of the collet is then pressed over onto the stone to secure the gem in place. Collets may be plain or decoratively enhanced with carving, piercing or millegraining.
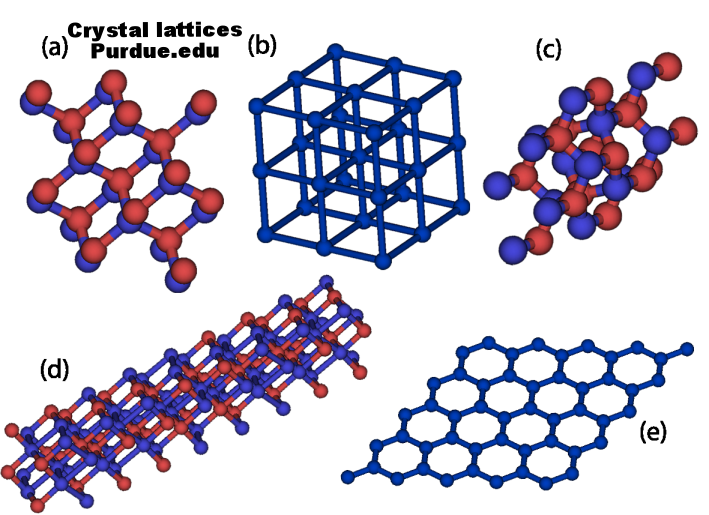
Crystal Structure and Lattice: The structure of all crystals may be described in terms of a lattice. The lattice is a group of atoms attached to every lattice point. When the arrangement is repeated in space it forms the crystal structure. A gem's overall crystal structure determines its symmetry, optical properties, cleavage planes, and overall geometric shape.
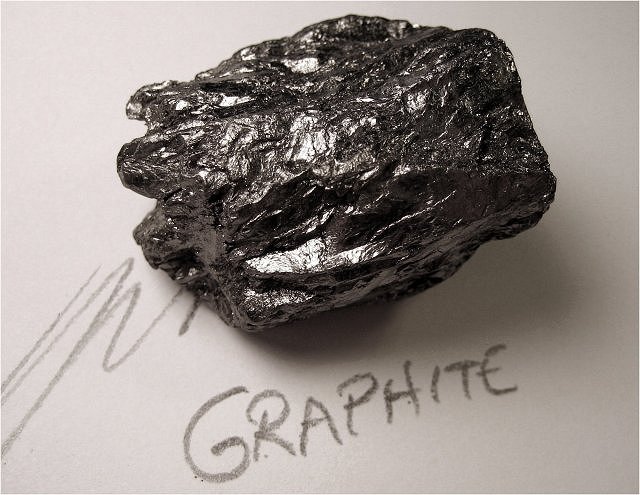
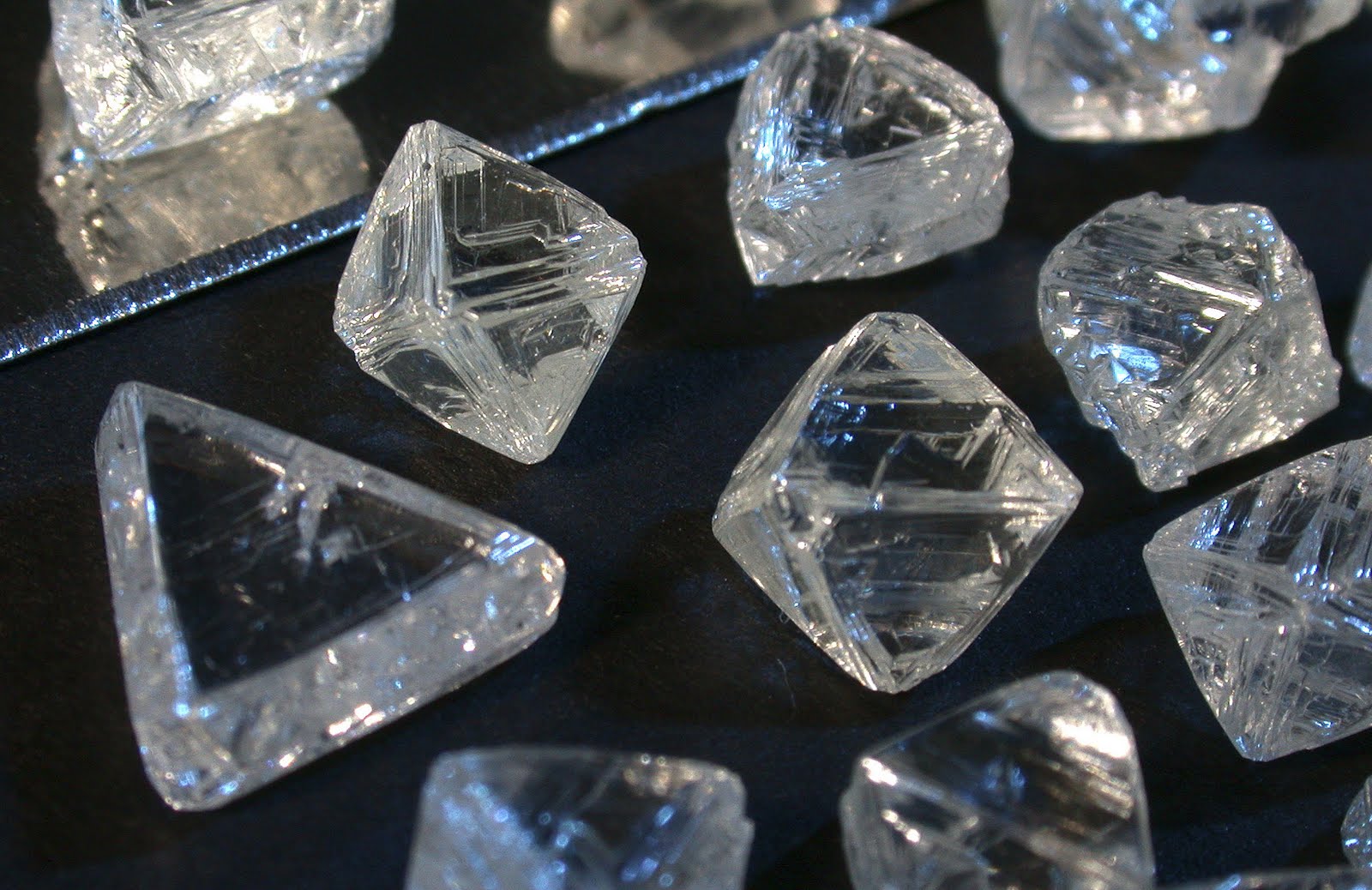
The arrangement of the atoms within the lattice can have a profound influence on the material's properties. For example, graphite and diamond each contain only one kind of atom, carbon. The only difference is in how those atoms are arranged.
Crystal Habit: The crystal structure is the blueprint for the crystal, the habit is the actual growth pattern of a crystals growth.
Crystal System: Generally crystal system/crystal family/lattice system each refer to one of several classes or groups of crystal formations that have similar symmetries (though there are many exceptions to this “rule”). In gemology there are 7 crystal systems.
Eye visible: Inclusions that an individual can see without the aid of a gemological tool such as a loupe or microscope.
Hardness: Refers to a materials resistance to indentation, scratching, cutting, and bending. A hard material will scratch a softer material. See Mohs Hardness Scale
Idiochromatic: An idiochromatic gem is one where the color is not due to impurities, but where the coloring element is an essential part of its chemical formula. An example of an idiochromatic gemstone is peridot, because iron is part of its makeup; no iron, no peridot.
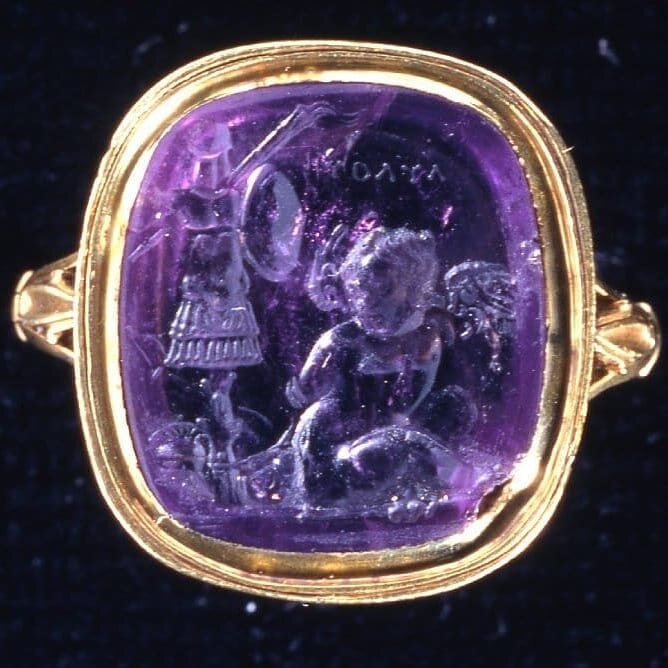
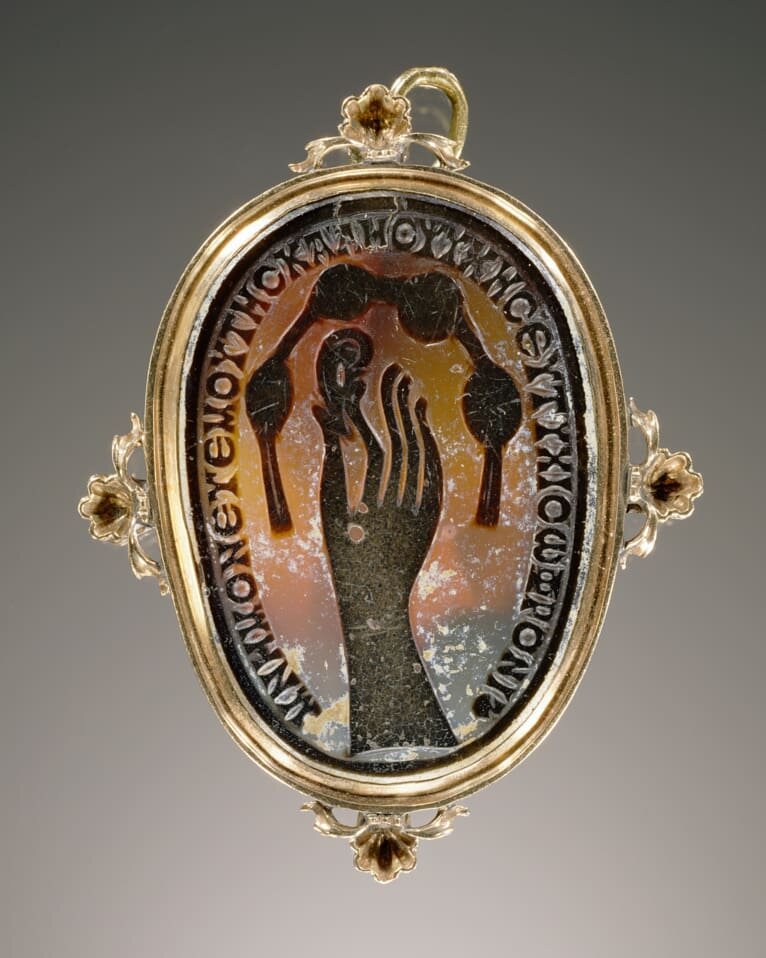
Intaglio:The carving or engraving of a design into a gemstone (the opposite of a cameo which is in high relief).
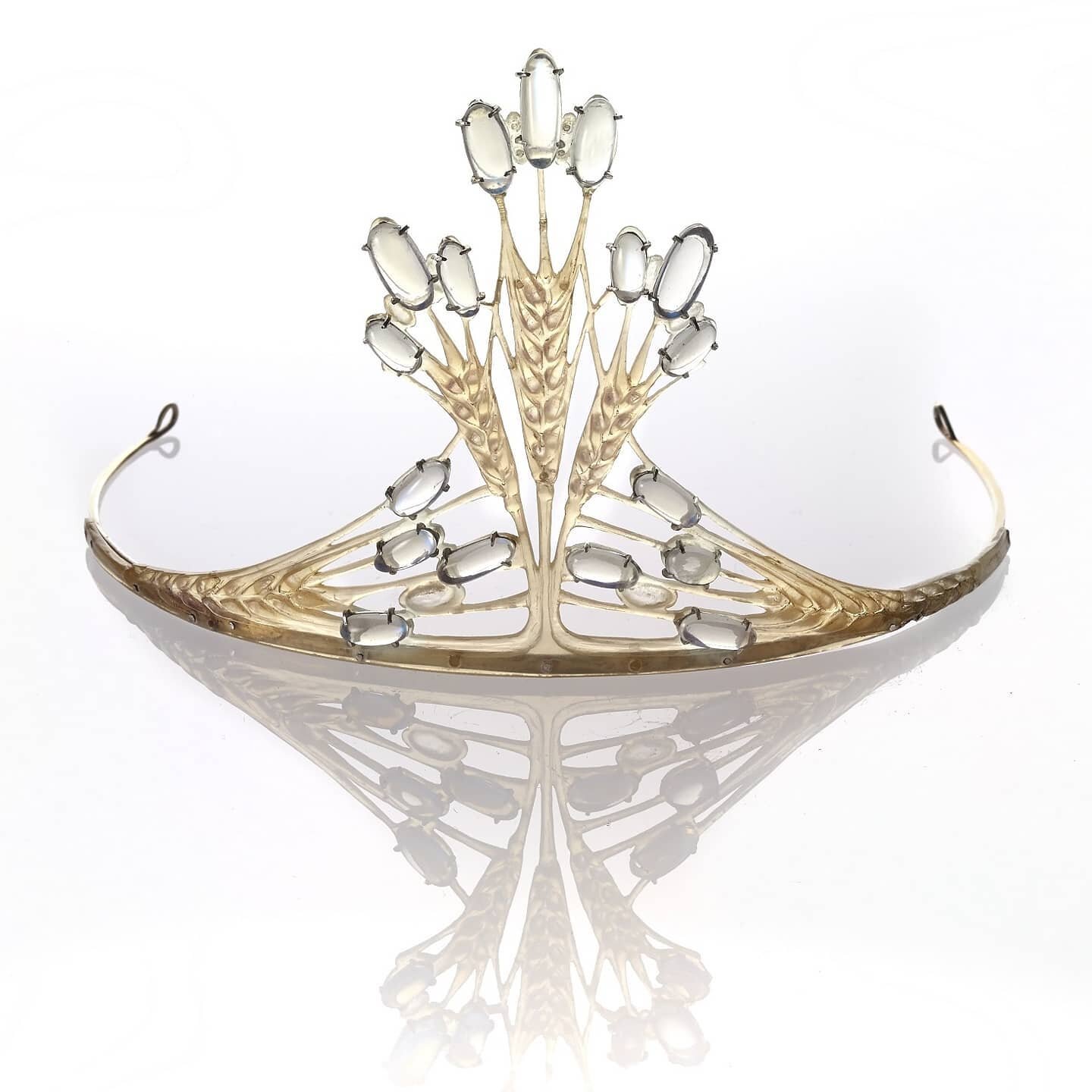
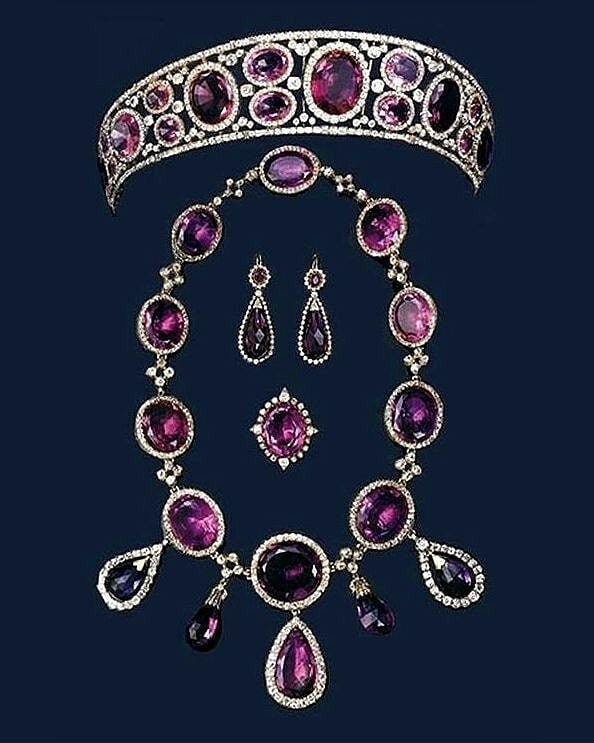
Kokoshnik: A kokoshnik traditional Russian headdress worn by women and girls, primarily worn in the northern regions of Russia in the 16th to 19th centuries. Kokoshnik tiara are modeled after the shape of this traditional headdress.
Lab-Created/Synthetic: These stones usually share the same chemical make up as their natural counterparts, but are “grown”/ created in a laboratory setting. ie lab grown sapphires, rubies, diamonds.
Macle or twinned diamond crystal
Macle: Macle is a term used to describe the most common type of twinned diamond crystal. It forms when crystal direction changes during growth to end up looking like a triangle. These stones are very shallow so they are not ideal for round brilliant cuts, however they are used for other shapes such as pears, triangles, and hearts. You might also see them set just as they are with all their natural beauty
Man-Made: Gemstones that are grown/created by humans. These stones may be synthetic in that they contain the same properties of the natural stone, or they may be simulants in that they just have the same appearance.
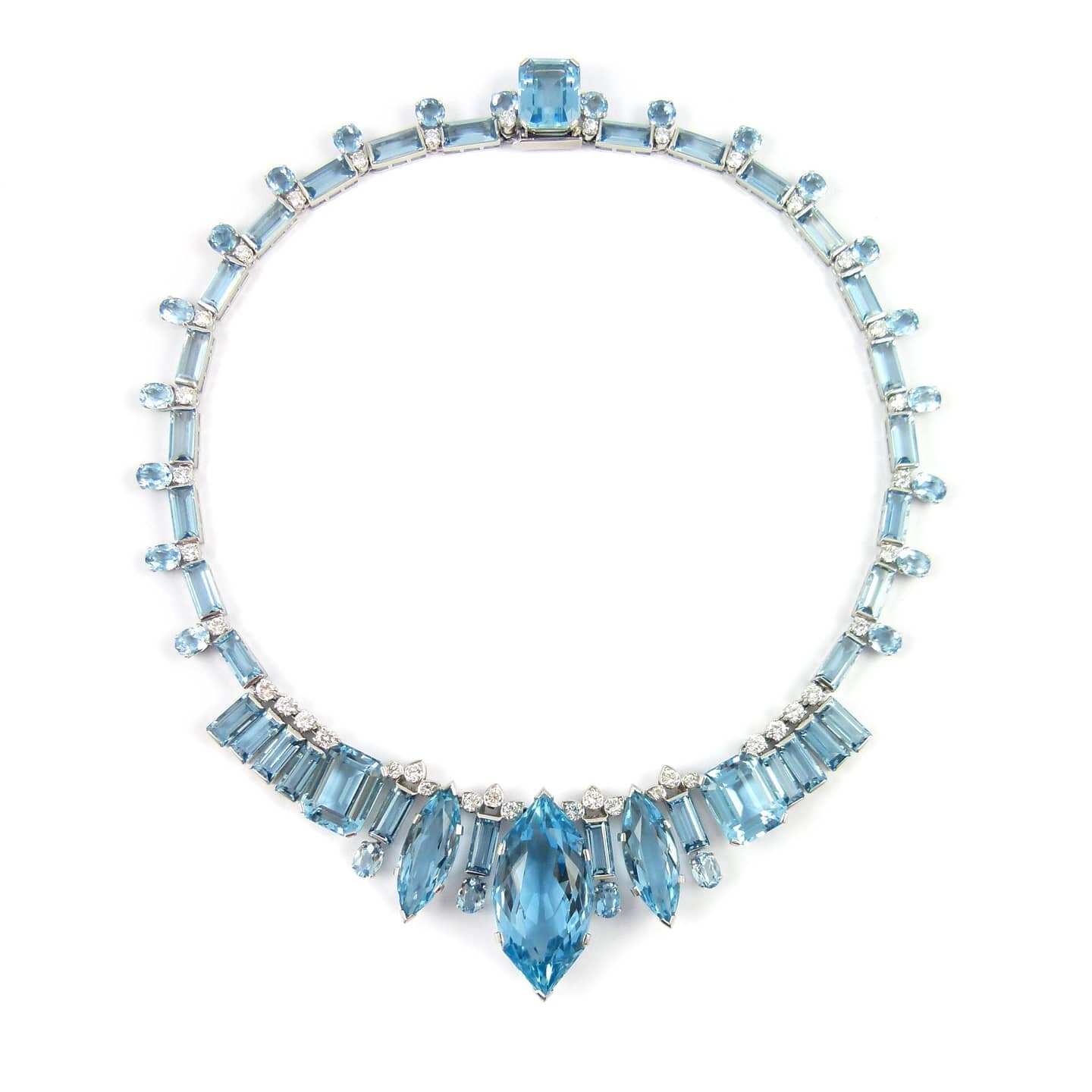
Navette: Navette is French for "little boat", because it resembles the hull of a sailboat. It is a term used to describe a gemstone or jewelry piece that is oval with a point at both ends. The alternate term for gemstones cut in this shape is marquise-cut.
Natural: Gemstones/minerals that are naturally occurring in the earth.
Pleochroic: Pleochroism is when a gemstone shows different colors in different crystal directions.
Simulant: A natural or man-made stone that has the same appearance as a natural gemstone but does not share the same properties. ie. white sapphire is open used to replace and simulant diamond. Gilson glass opals are a man-made simulant of opal.
Toughness: Refers to the way that a material reacts to impact. Toughness is a combination of high strength and medium ductility. Essentially the materials resistance to fracture when stressed. For example Jade does not have high hardness and is there for easily carved, however it has high toughness and has been used for items such as hand axes and knives.